1
About Operating System
In this chapter...
Here are the topics we'll cover
Operating Systems
An operating system (OS) is a program that acts as an intermediary between the user of a computer and the computer harware. The purpose of an operating system is to provide an envirnment in which a user can exicute programs in a convenient and effective manner.
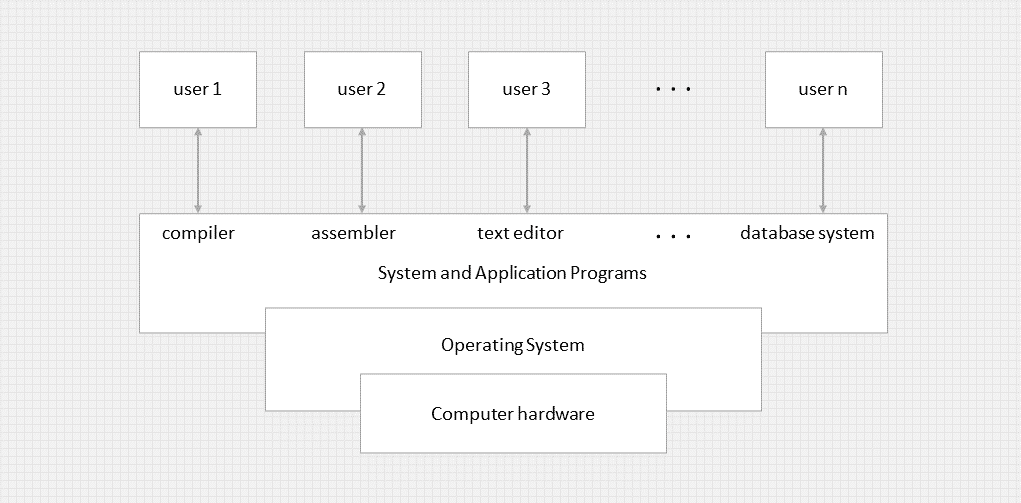
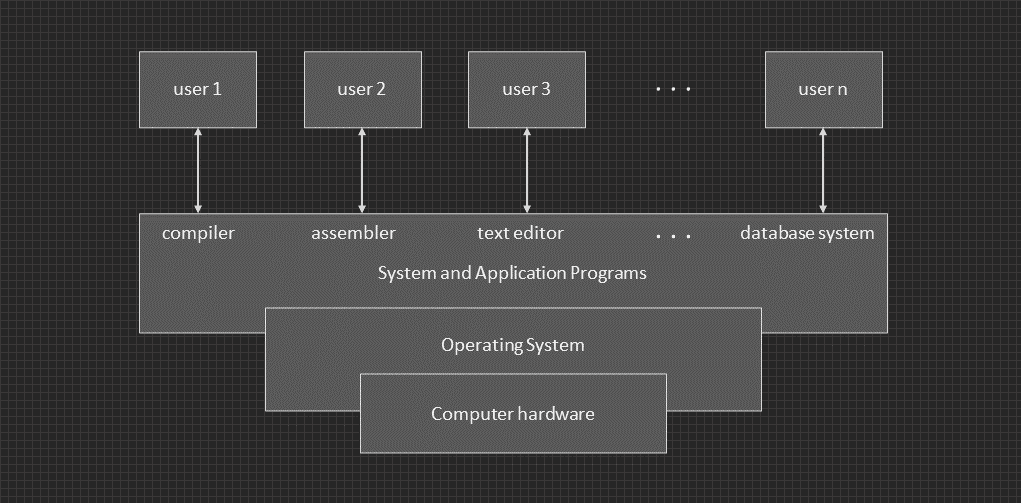
Abstract view of a computer system.
A computer system can be devided roughly into four components: the hardware, the operating system, the aplication programs, and the users.
Because an operating system is large and complex, it must be created piece by piece. Each of these pieces should be a well-defineated portion of the system, with carefully defined inputs, outputs, and functions.
Operating System functions
Operating System perform lots of manageriable activites but some of them followings are listed below —
-
Main Memory Management: The Memory Manager is in charge of main memory, also known as Random Access Memory (RAM) . The Memory manager checks the validity of each request for memory space and, if it is a legal request, it allocayes a portion of memory that isn't already in use.
A primary responsibility of the Memory Manager is to protact the space in main memory occupied by the operating system itself. It can't allow any part of it to be accidentally or intentionally altered.
-
Processor Management: The Processor Management decides how to allocate the Central Processing Unit (CPU). An important function is to keep track of the status of each process. Here, the process is known as an instance of execution of a program.
The Processor manager monitors whether the CPU is executing a process or waiting for a READ or WRITE command to finish execution. It has two levels of responsibility. One is to handle jobs as they enter th system and the other is to manage each process within those jobs. i.e. First part is handled by the Job Sheduler and Second part is handled by the Process Sheduler.
-
Device Management: The Device Manager monitors every device, channel, and control unit. Its job are to choose the most efficient way to allocate all of the system's devices like as printers, ports, disk drives, etc. all the policies chosen by the system designers.
The Device Manager does this by allocating each resource, starting its operation, and finally deallocating the device, make sure for available to the next process or job.
-
File Management: The File Manager keeps track of every file in the system, includeing data files, program files, compilers, and applications. The File Manager also controls what users are allowed to do with files once they access them. It allocates the necessary resources and later deallocates them.
-
Network Management: Operating Systems with Internet or networking capability have a fifth essential manager called the Network Manager that provides a convenient way for users to share resources while controlling users access to them.
-
User Interface: The User Interface is the portion of the operating system that users interact with directly. This can be done by the Graphical User Interface (GUI) or Command-Line Interface (CLI) or both together.
Classification of Operating Systems
Next Up
2: Operating System Structure
Let's know structures of operating system and different Kernels.
Start Chapter 2 ➔