6
Networking
In the privious chapter we have learn about the how JavaScript is important for the web development, Some basic methods and objects which are frequently used in web pages.
In this chapter...
Here are the topics we'll cover
What is internet addressing and their versions.
Understanding the factory function and instance method.
Learn about the TCP/IP client sockets.
Understanding the URL and URL connection.
Learn about the TCP/IP server sockets.
Understanding the Datagram.
IP Address
The Internet Protocol is the network layer protocol responsible for maintaining the endpoint of the an Internet connexion. IP defends the addressing his scheme used by TCP Packets and the encapsulation of the data into the datagram format that is transported over a network. IP is a stateful, but connectionless protocol. i.e While the endpoints are known and can be either real or virtual, the path between the endpoints is left undefined.
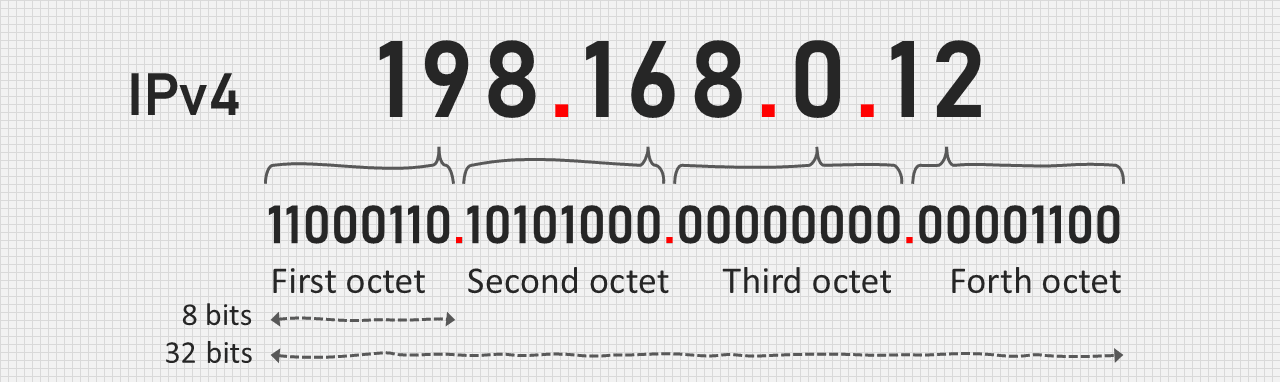
IP address stands for Internet Protocol Address. An IP address is the unique number provided to each and every devices. An IP address is the identifier that enables your device to send or receive data packets across the Internet. It holds information related to your location and therefore making devices available for two way communication.
The Internet required a process to distinguish between different networks, routes and websites. Therefore IP address provide a mechanism of doing so, and it forms an independible working part of the Internet. It is in the form of integrate number which is separated by dot.
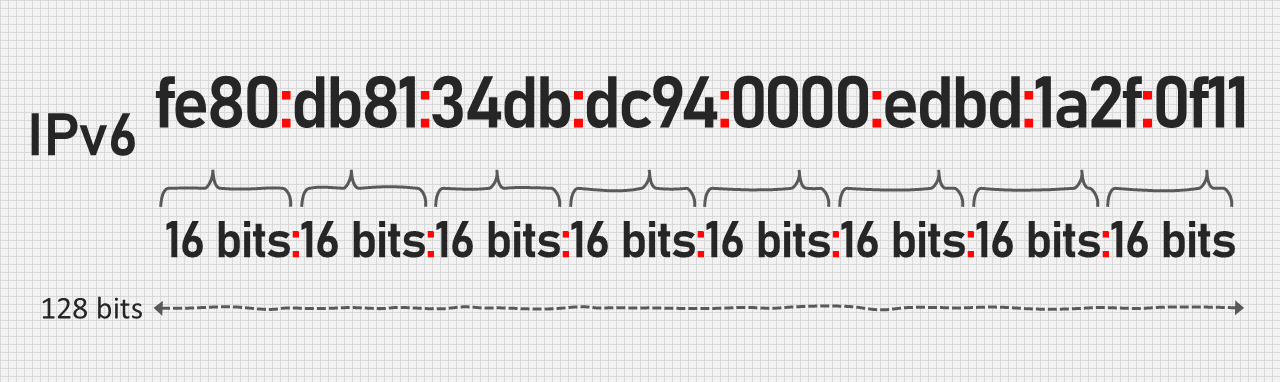
Difference between IPv4 and IPv6—
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|
| IPv4 address are 32-bits long i.e. it 4 octets and each octet are fixed is 8-bit in size. | IPv6 address 128-bits long i.e. it contains 8 feasible or octets and each octate is 16-bit in size. |
| IPv4 encryption and declaration node implementated in protocol version 4. | Encryption and Authentication are implemented in protocol version 6. |
| IPv4 consists of 4 octet and address is represented in dot-decimal. | IPv6 consists of 8 field and each field includes 2 octets. Hence, total number of octets= 6 and address is represented in hexadecimal. |
| IPv4 has the broadcast information transmission scheme. | IPv6 follows a multicasting transmission scheme which provides efficient network service. |
| In IPv4 the number that every field holds should be in the range of 0 to 255. | In IPv6 each hexadecimal character denotes 4-bits. so a user is required to convert 4-bits to a hexadecimal number at a time. |
IP Address octets in IPv4 diagram
IP Address octets in IPv6 diagram
Factory Function
A factory function is a function that returns a new Instance of a class or object. Insted of directly calling a class constructor to create an object, A factory function abstracts the object creating process, often adding additional logic or configurations.
Here's a sample example of a factory function.
Hello, I'm Prince, I'm 22 years.old, and I study Compuetr Science.
Hello, I'm Yash, I'm 21 years.old, and I study Information Technology.Instance method
An instance methods play a crucial role in web technology, particularly in the context of object-oriented programming in web development. They allows us to define behaviors of objects and interact with the data contained within those objects.
Instance methods are often used within classes to define object behaviors. Here's an example given below—
Username: mohemohe.in, Email: info@mohemoe.in
Email updated to inf@mohemohe.org
Username: mohemohe.in, Email: info@mohemoe.orgTCP/IP Client Sockets
TCP/IP client scokets are used to create network connections between a client and a server. They enable communication over TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), which is a reliable, connecting-oriented protocol used by many applications for data transfer.
Here's an example of TCP/IP client scoket using the node.js with net module—
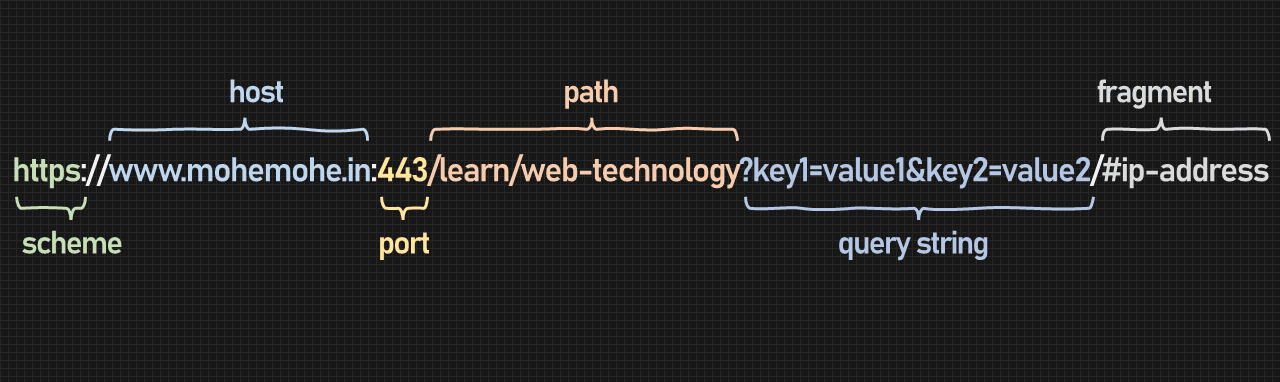
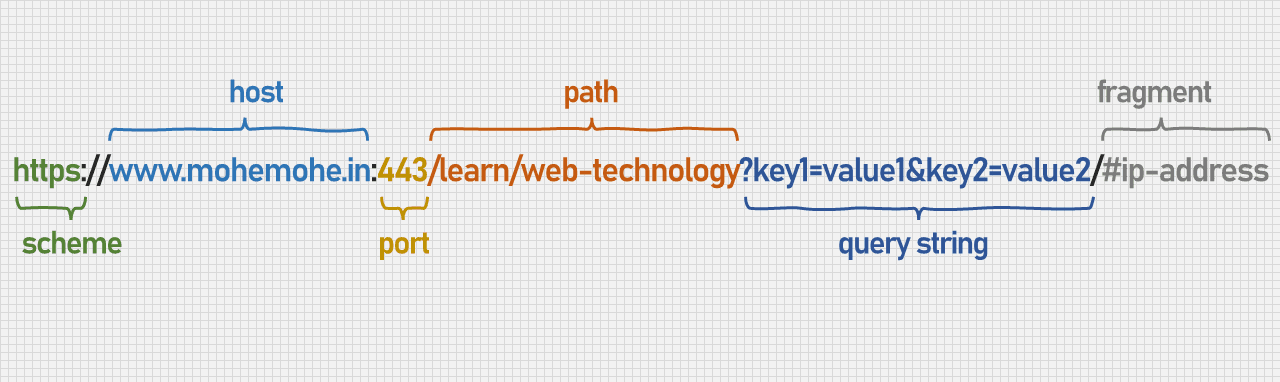
URL
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is essentially the web address used to access resources on the internet. It points toh the location of a resource, such as a web page, image, video, or file.
Here's an example of url:
Uniform Resource Locator (URL) diagram
Scheme: https indicates that the resource should be accessed using the HTTPS protocol. (e.g. http, https, ftp).
Host: www.mohemohe.in is the domain name that points to the serer where the resouce is hosted.
Port: 443 specifies the port number used by the https protocol. This part is optional and often implied by the scheme. (e.g. 80, 443).
Path: /learn/web-technology specifies the exact location of the resource on the server.
Query String: key1=value1&key2=value2 passes additional parameters to the server.
Fragment: #ip-address direct the browser to a specific part of the resource, such as an anchor on a webpage.
URL connection
Connecting to a URL is a common operation in many programming languages, often used to download data, interact with web APIs, or scrape web pages.
Using the HttpURLConnection class to connect to a URL in Java language. Here's an example given below—
TCP/IP server sockets
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is a suite of communication protocol used to connect devices on the Internet and local networks. TCP/IP server socket allows a server to listen for incoming connection requests from clients and facilitate bidirectional communication over a network.
Socket: A Socket is an endpoint for communication between two machines. It is identified by an IP address and a port number.
Server Socket: A server socket is a special type of socket that wait for incoming connection requests from client sockets. Once a connection is established, the server socket can communicate with the client socket.
Use Cases
- Web Servers: Serving web pages and handling HTTP requests.
- File Transfer: Transferring files between devices.
- Chat Applications: Enabling real-time communication between users.
- Remote Access: Providing remote access to servers and devices.
Advantages
- Reliability: Ensures data is deliberate accurately in the correct order.
- Error Detection: Uses checksums to detect errors in transmitted data.
- Flow Control: Manages data flow to prevent network congestion and ensure efficient data transfer.
- Bidirectional communication: Allows two-way communication between the server and clients.
Datagram
Datagram are collection of information sent from one device to another deviceviathe established network. When the datagram is sent to the targeted devicethere is no assurancethat it will reach to the target devicesafely and completely. The udp protocol is used to implement the Datagrams in Java.