4
Cascading Style Sheet
We have learned HTML in privious chapter Chapter 2, there was simple markup language. and if we want to desgin user interface (UI), we need to use something different that is style sheet, it offer control over the layout. Style sheet are the best approach for creating attractive pages.
In this chapter...
Here are the topics we'll cover
Why css is important.
CSS Selector and Type of Selector.
Study about Advanced CSS that are more attractive the the basic CSS, that have a lot of features.
Structure and Layout of the website according to different systems.
CSS
Cascading Style Sheets are a standards-based mechanism for suggesting presentational style (e.g. font, colour, layout) for the HTML documents. CSS is a flexible and cross-platform and is designed to preserve the accessibility of the document's structural content.
Cascading Style Sheets were developed as means for creating a constant approach to providing a style information for the web document.
Style rule
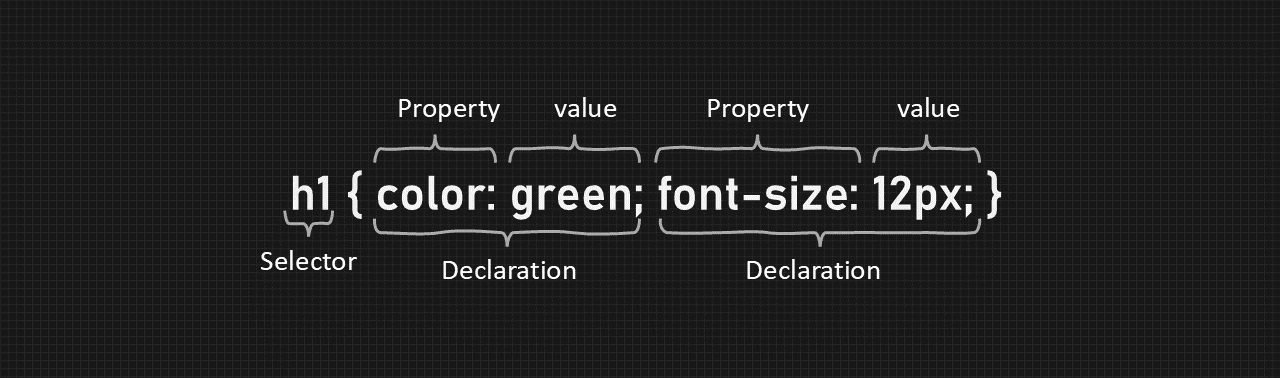
Style rule is set of HTML tags specifing the formatting elements. It can be applied to selected content of the web page. A style rule can be split into two parts—
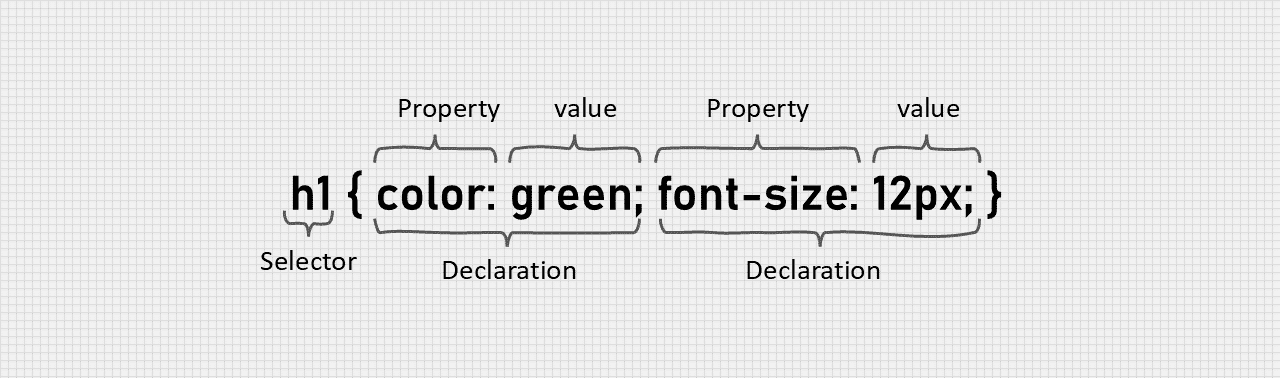
CSS Syntax diagram
Here, h1 is selector color is property green is property value & font-size is property and 12px is value.
Selector: The selector pointer to the HTML element we want to style.
Declaration: The decleration pop contains one or more decleration saperated by semicolons.
Each decleration includes are CSS property name and a value saperated by a colon :.
Saperator: Multiple CSS decleration are saperated with semicolons ; and decleration are surrounded by curly bracess { }.
CSS Comments
Comments are used to explain the code and may help when you read the source code at a letter date, components are ignored by the browser. A CSS comment is a placed inside the <style> element. Starts with /* and in ends with */.
p {
color: pink; /* text color will be change into pink */
text-align: center; /* text will be align in center */
}CSS properties
color: Changing the text color, value, equivalent to all color.
text-align: Changing alignment of text. (value: center, left, right).
font-family: Changing the font type. (value: All fonts name)
background-image: Setting back ground of the image.
font-style: Changing the font style.
font-weight: Setting font weight like bolder, lighter (value: bold, light, normal).
background-color: Setting background color of webpage.
word-spacing: Set the space between the words.
letter-spacing: Setting space between charecters.
text-decoration: Decorate the text. (value: blink, underline, overline)
text-transdorm: It is used to convert the text capital to small and viceversa.
CSS Styling
CSS styling refer to the overall process of complaints css property to HTML element to achieve desired look and feel.
background
color: Denotes colour property, used to set text colour.
background-color: This property sets an element's background colour.
background-image: Associates a background image with an element.
background-position: A specifies how a background image is positioned.
Text Format
latter-spacing: Denotes the space between letter the default value of A, variety of measurements like inches (in), centimetre (cm), millimetre (mm), points (pt) etc., can be used.
word-spacing: Denotes the space between words. Measurement can be used similar to letter-spacing.
vertical-align: Denotes the vertical positioning of the text and images, with respect to the baseline. The possible value include baseline, sub, super, top, text-top middle percentage value etc.
text-align: Specifies the alignment of the text. The possible values are centre, justify etc.
text-indent: Denotes margins. This properties sets the indentation for the text in the first line of the block level of element.
text-transform: Denotes the transformation of text. The possible values are Capitalised, UPPERCASE, lowercase etc.
text-decorate: Denotes the text declaration. The standard value at this property include blink, line-through, overline, underline etc.
Controlling Fonts
font-family: Denotes font
font-size: Denotes the size of the text
font-style: Denotes the style of the text for example normal, bold, italic etc.
font-weight: Denotes the weight or darkness of the font. This value ranges from 100 to 900 increment of 100.
CSS Selector
CSS selector are used to find or select HTML element based on their element name, id, class attribute and more. Some selectors are listed below —
The Universal Selector
Rather then selecting elements of a specific type the universal selector quite simply matches the name of any element type.
* {color: green;}The Element Selector
The element selecotr selects elements based on the element name. You can select all p element on a page like this.
p {text-align: center; color: blue;}The Descendant Selector
It is used when developer wants to apply a style rule to a particular elements only when it lies inside a particular elements.
ol p {color: green;}Id Selector
It can be used identify one element. In CSS and id selector is a name preceded by hash # symbol.
#id_selector_name {property: value;}Class Selector
It can be used to identify more than one element. In CSS, a class selector is a name proceded by dot . symbol .
.class_selector_name { property: value; }Differences between id and class
id | class |
|---|---|
| IDs must be unique | Classes can be used on multiple elements. |
| ID selectors have higher specificity than class selectors | Class selectors have lower specificity than id selecotr. |
| IDs will override those applied with classes if both are used | Class selecotr cann't be override the ID selecotr |
Types of CSS
There are three types of CSS which are given below or Three ways of inserting a style sheet —
- Inline CSS: It contains css property in the body saction attached with element is known as internal css. This kind of style is specify within an HTML tags using their style attribute.
<p style="color: pink"> Welcome to CSS </p> - Internal CSS: It is used to apply css on a single document or page. It can affect all the element of the page. It is written inside the
<style>tag which in<head>section of the HTML. - External CSS: It is used to apply css on multiple pages or all pages. It can be written in any text editor. The file should not contain any
<html>tags. The file must be saved in with.cssextension.
Block elements and object
Block level elements who behave like blocks. e.g. <p>, <h1>, <ol>, <ul>, <address>, etc.
These elements always starts in newline and occupied full width of parent element.
Block element contain both inline element and block element.
| Element Name | code | use |
|---|---|---|
| para tag | <p> </p> | create new paragraph. |
| pre tag | <pre> </pre> | create pre formated. |
| hr tag | <hr> | horizontal rule used to break with 2px gradiant shadow. |
| block quote | <block qoute> </block quote> | create block quote from new line. |
| division tag | <div> </div> | create new division. |
| unordered list tag | <ul> </ul> | create unordered list. |
| ordered list tag | <ol> </ol> | create ordered list. |
| address tag | <address> </address> | create postal address. |
| headings | <h1> </h1> till <h6> </h6> | create headings and sub heading. |
| form tag | <form> </form> | used to send form data. |
List and Table
List
CSS provides several properties to style HTML list, which can be either ordered <ol> or unordered <ul>. Here are some key properties and a technique.
list-style-type: Specifies the type of list item marker.
ul { list-style-type: square; }
ol { list-style-type: upper-roman; }list-style-images: Uses an image has the least item marker.
ul { list-style-position: inside; }list-style-position: Specifies the position of the list item markers (inside or outside).
ul { list-style-position: inside; }list-style: A shorthand property of setting list-style-type, list-type-position and list-style-image in one declaration.
ul {
list-style: square inside url('bullet.png');
}Table
CSS can a significantly enhance the appearance of estimated tables. Here are the some common properties and techniques.
border: Adds borders to the table, rows, and cells.
table, th, td { border: 1px solid black; }border-collapse: Collect the borders into a single border.
table { border-collapse: collapse; }width: Sets the width of the table.
table { width: 100%}padding: Adds padding inside the table cells.
th, td { padding: 10px; }text-align: Aligns the text inside the tbale cells.
th, td { text-align: left; }Box Model
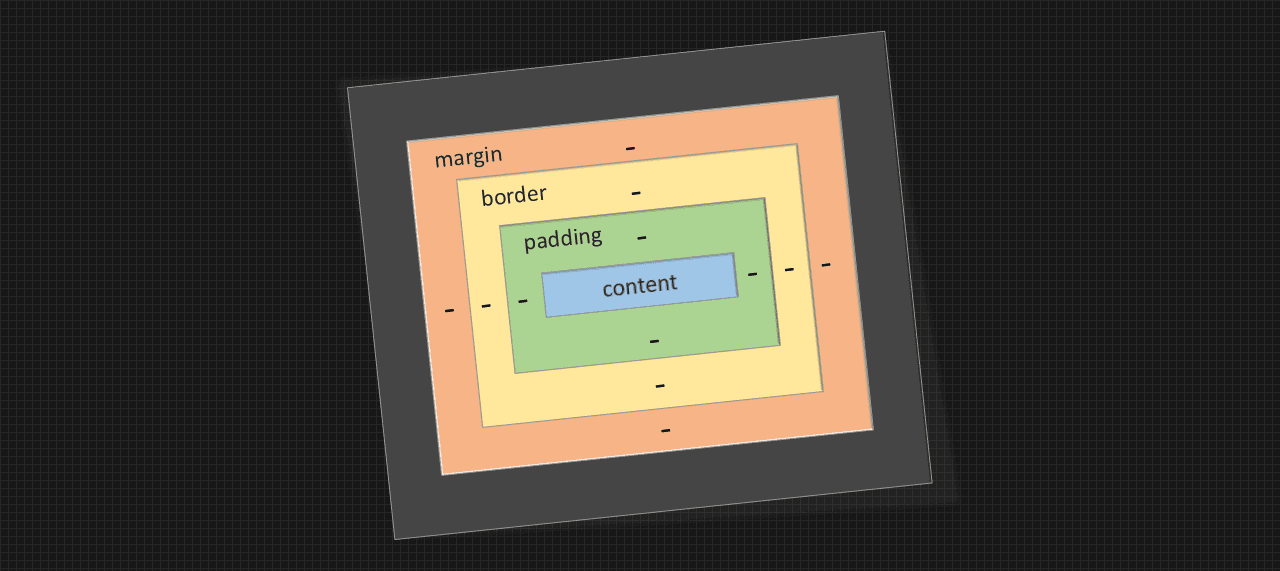
The CSS box model is essentially a box that wrap around every html element it consists of margin border padding and the actual content.
In CSS the term box model is used when talking about design and layout.
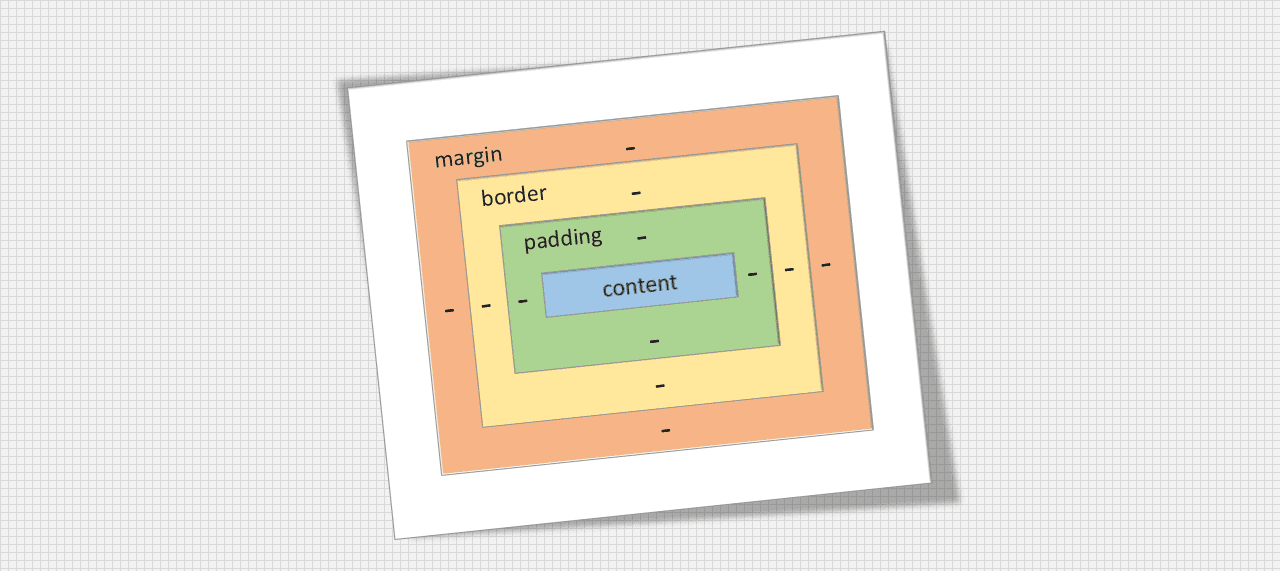
CSS Box Model diagram
content: The content of the box vertex and image appear.
padding: It clears an area around the content. The padding is transparent.
border: A border that goes around the padding and content.
marging: It clears an area outside the border. The margin is transparent.
For Total Width
Total width = content width + (left + right) padding + (left + right) border
For Total Height
Total height = content height + (top + bottom) padding + (top + bottom) border
CSS Border
CSS border properties allow you to specify the style, width and color of an element border.
border-style: This property specifies what kind of model to display. (value: dotted, dashed, solid, double, groove, ridge, insect, outset, no-border, hidden-border)
border-width: It is used to set the borders width in pixels. You can also use predefined value like thin medium or thik to set the width of the border.
CSS Advanced
Advanced CSS refers to the use of sophisticated technique and tools to create highly customised, responsive and visually appealing web pages it goes beyond basic styling capability like font colours and margins incorporating more complex concepts.
| CSS version | Description |
|---|---|
| CSS1 | Religion in December 1996 CSS1 introduced basic styling capabilities such as font, color, and spacing. |
| CSS2 | Religion in May 1998, CSS2 added more sophisticated features like absolute, relative, and fixed position, z-index, and media types. |
| CSS2.1 | An update to CSS to CSS2.1 was finalised in 2011, refining and fixing issue from CSS2. |
| CSS3 | Unlike previous version CSS3 is divided into modules, each focusing on a specific aspect of CSS (e.g. flexbox, Grid, Animations). This more approach allows for more flexible and faster development. |
| Current State | Instead of a single virsion, CSS is now developed as individual modules, each with its own version number. (e.g. the CSS grid layout module is at level 1, while CSS colour module is at level 5). |
Grouping
Grouping in CSS is a technique used to reduce code redundancy and write clean, concise, easy to follow code. These are many instance in which multiple css selector will have same declaration. In this cases, we can group all the selectors together and write their declaration only one time. e.g.
Dimensions
It is defined as the border that surrounds every box i.e. element padding that can appear inside each box and the margin that can go around them.
Along properties allows us to control the dimensions of a box —
height and width: It allows us to set the height and width for boxes, they can take value of length, a percent or the keyword.
line-height: It allows us to increase the space between lines of the text. The value of line height property can be a number, a length, a percentage.
max-height: It allows us to specify maximum height of a box. The value of maximum height property can be a number, a length or a percentage.
min-height: It allows us to specify minimum height of a box. The value of minimum height property can be a number, a length or a percentage.
max-width: It allows us to specify maximum width of a box. The value of maximum width property can be a number length or a percentage.
min-width: It allows us to specify minimum width of a box. The value of minimum width property can be a number length or a percentage.
Display
It allows us to control the display of HTML element by using the display visibility property. The display property specifies how to display an element while the visibility property specify whether should be hidden or visible.
The display property is used to display element specify in manner. It generates the particular type of box of an element. This property take different value in which inline, block and none are most common.
The feasibility property is specifies whether an element is visible or a web based or node it takes four value visible, hidden, collapse and inherit.
Positioning
This property is specified how an element is partitioned in a document. The top, right, bottom and left property define the location of positioned element.
There are following five different position value given below—
position: static;: By default HTML element are positioned static. they are not affected by top, bottom, left and right property. The static is always positioned according to the normal flow of the page.
position: relative;: The box position is calculated according to the normal flow by applying the properties top, right, bottom and left. The relatively positioned element will cause it to be adjust away from its normal position. Other content will not be adjusted to fit into any gap left by the element.
position: absolute;: The box is taken out of the normal flow. The box position is specified with the top, right, bottom and left.
position: fixed;: The element is positioned relative to the viewport, which means it stays is the same place even when the page is scrolled.
position: static;: The element is targeted as relative until it crosses a specific threshold, at which point it is treated as fixed this is useful for creating elements that stick on the viewport as we scroll.
Floating
Css allows us to implement the text feature into web page by using the float property. This property means an HTML element has a floated element defines the side where other element are display.
float: [value];The float property supports the following value —
left: Float an elements to the left to respect to the content.
right: Float an element to the right to respect to the content.
none: Doesn't flow an element.
Pseudo Class
Pseudo classes are predefined class that enable to able apply certain styling, rule or a specific state of an element. These classes allow to style, visit or unvisited links, or to specify how to link or redirected in response to user actions.
Pseudo element referred to subpart of the element such as the first letter of paragraph. Pseudo classes and pseudo elements allow us to style the first line of the paragraph and first letter of a word.
Pseudo classes are used to at special effect to the selectors such as changing the colour of the visited links.
The selectors are the name, given to different style. A pseudo class always start with colon :.
Here are some common pseudo-classes—
:hover: Applies when the user designates an element (usually with a pointing devices), but does not activate.
:active: Applies while an element is being activated (e.g. when a button is being clicked).
:focus: Applies when an element has received focus (e.g. when an user click on an input field).
:visited: Applies once a link has visited.
first-child: Applies to the first child of a parent element.
:last-child: Applies to the last child of a parent element.
:nth-child(n): Applies to the nth child of a parent element.
:not(selector): Applies to element that do not match the specified selector.
CSS Navigation Bar
In CSS, a navigation bar is also known as nav bar. which is used in an interface to provide navigation link or menus to the various selectors or page users in website design.
User can easily navigate a website content using it as a visual guide with the help of a navigation bar. We can improve the presentation and styling of the Web page and it also include design,color, fonts and spacing descrived using CSS.
Here's a basic example of how to create a horizontal naviagation bar.
Resposive navigation bar
To make the navigation bar responsive, we can use media query to adjust their layout for different screen sizes. Here is an example—
Image Sprites
It is a collection of images put into a single image. A web page with many images can take a long time to load and generates multiple server request. Using image strips will reduce the number of server requests and save bandwidth.
Here's an example of how to use image sprites in CSS
Benefits of using it
Reduced HTTP Requests: By combining multiple images into one, we reduced number of HTTPRequests, which can improve page load time.
Improved Performance: Fewer requests means less overhead and faster rendering of the page.
Simplified Maintenance: Managing a single sprite image can be easier than handling multiple individual images.
Atrribute selector
CSS attribute selected allows us to select HTML element based on the presence of value of their attribute. There are the different type of attributes selected and how they work—
[attribute]: Selects elements with the specified attribute. Here selects all <a> elements with a target attribute.
[arrribute="value"]: Selects elements with the specified attribute the value. Here selects all <a> elements with a target attribute value of _blank.
[attribute~="value"]: Selects elements with an attribute value containing a specified word (space-sperated list). Here selects elements with a title attribute that contains the word "flower".
[attribute|="value"]: Selects elements with an attribute value that is exactly the specified value or starts with the specified value followed by a hyphen. Here selects elements with a class attribute value of "top" or starting with "top-".
[attribute^="value"]: Selects the elements with an attribute value that starts with the specified value. Here selects with a class attribute value that starts with adject with "top".
[attribute$="value"]: Selects elements with an attribute value that ends with specified value. Here selects elements with a class attribute value that eds with "test".
[attribute*="value"]: Selects elements with an attribute value that contains the specified value. Here selects elements with a class attribute value that contains "te".
CSS Color
The color property specify the color of text. It accept value like named colors: RGB, RGBA, HSL and HSLA. This property plays a crucial role in defining text appearance, ensuring readability and enhancing the overall design of web content.
color: It will set the colour to the text which the programmer specifies in the css file. The color can be set to the text in the foreground.color: [name]: By directly specifing the name of the colour like blue, green, pink, tomato, etc.
They are the following color property value given below—
RGB value: Here R stand for RED, G stand for Green and B stand for Blue. The colour will be assigned to the text by using the range of these values. The values in this form (0 - 255).
RGB(255, 0, 0) /*RED*/
RGB(0, 255, 0) /*GREEN*/
RGB(0, 0, 255) /*BLUE*/Hexadecimal value: It represents the value of the colour in hexadecimal format. It should start with the prefix #. These values ranges from #000000 to #ffffff.
HSL value: HSL stand for the Hue, Saturation, Lightness. The range of the hue will be from 0° to 360°. Saturation means the grey effect and its ranges from 0% to 100% and lightness means the effect of light which range from 0% to 100%.
CSS Website Layout
A website layout prefer to the saturated arrangement on a web page using CSS. This includes the positioning of headers, footers, sidebars, content area and other graphical element to create a coherent and visual appearing interface.
It plays a crucial role in defining its visual structure, organisation and responsiveness when design a website.
A website can be divided into various sections comparison of header, menus, content and footer based on which there are many different layout designs available for developers.
Different layouts can be created by using a <div> tag and using css property.
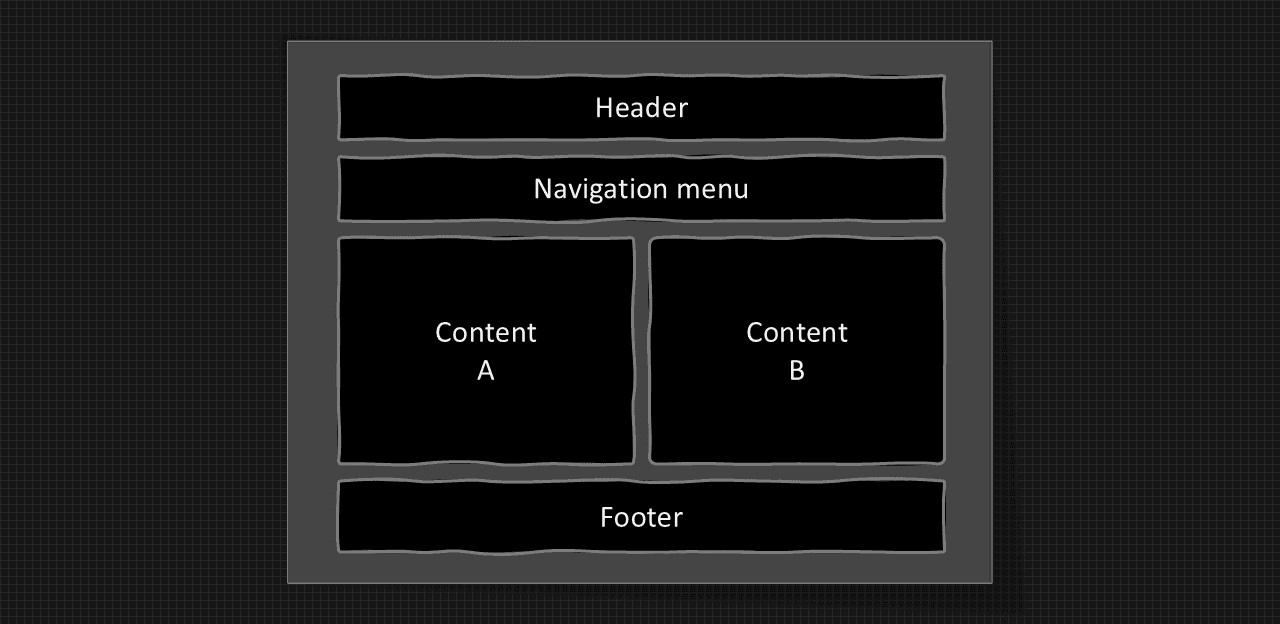
Structure of website layout
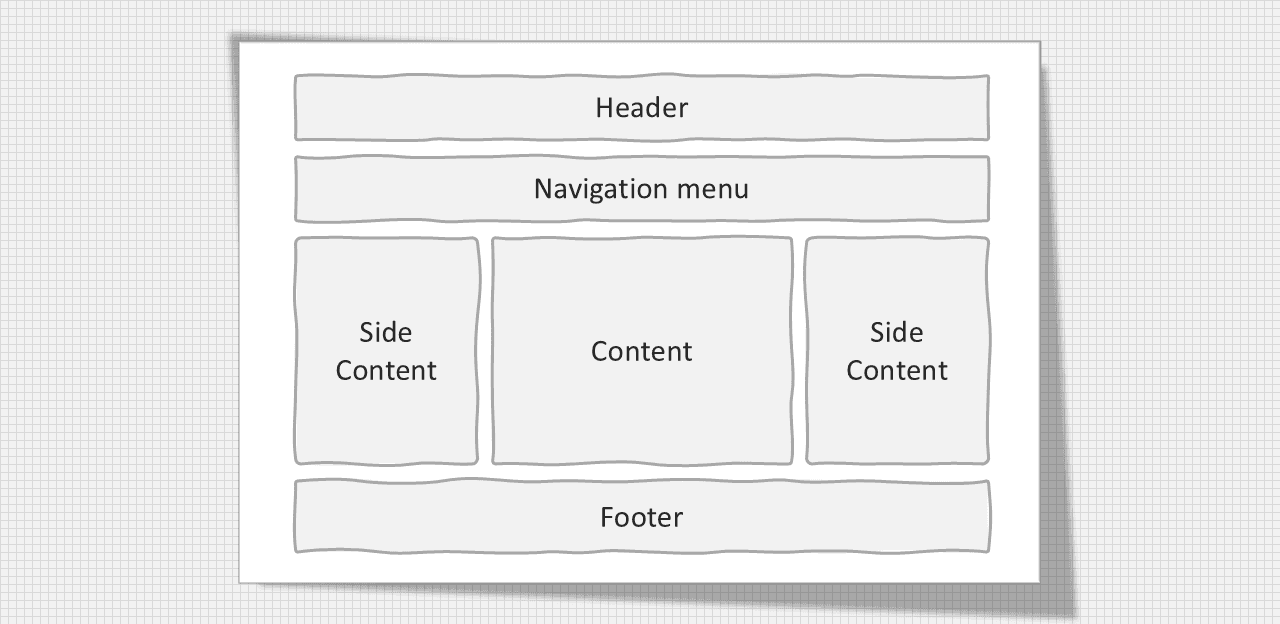
Structure of website layout.
Header Section: The header section typically appears at the top of website or just below the top of navigation menu. it offers include name or logo.
Navigation menu: The Navigation menu provide link for easy website navigation.
Content Section: The content section is the main body of the website. The user can divide the content section into column layout.
Footer Section: The Fotter Section appears at the bottom of the website.
The most common layout
These are the following common layout —
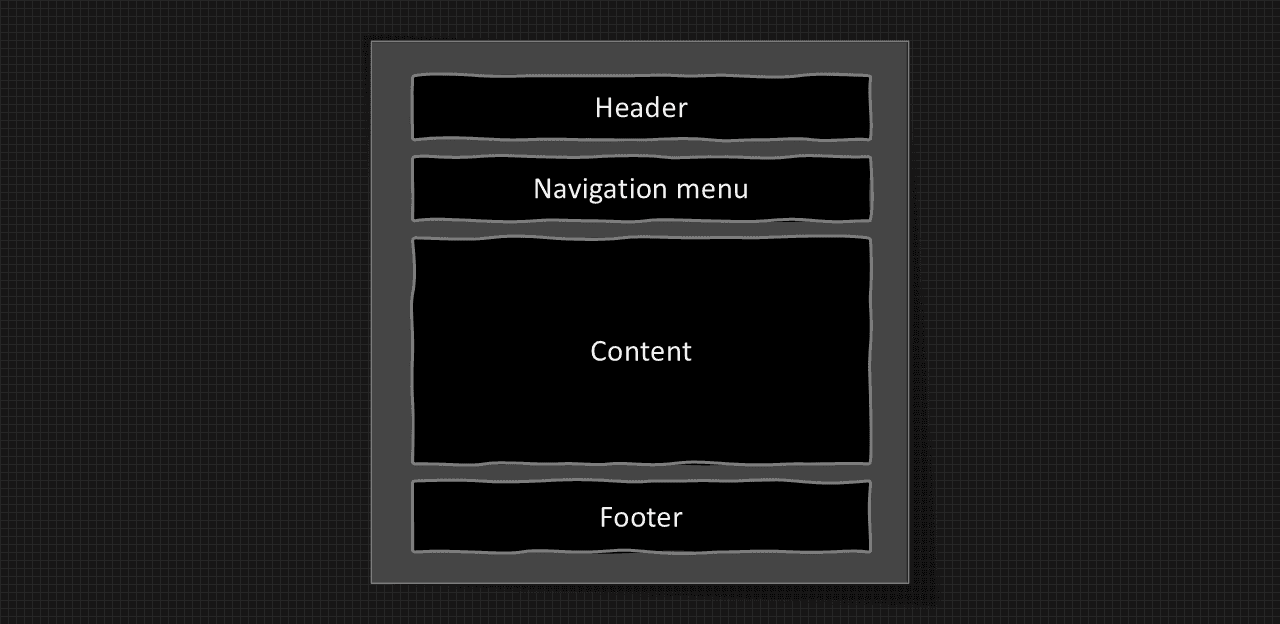
One column layout: It is commonly used for mobile layout.
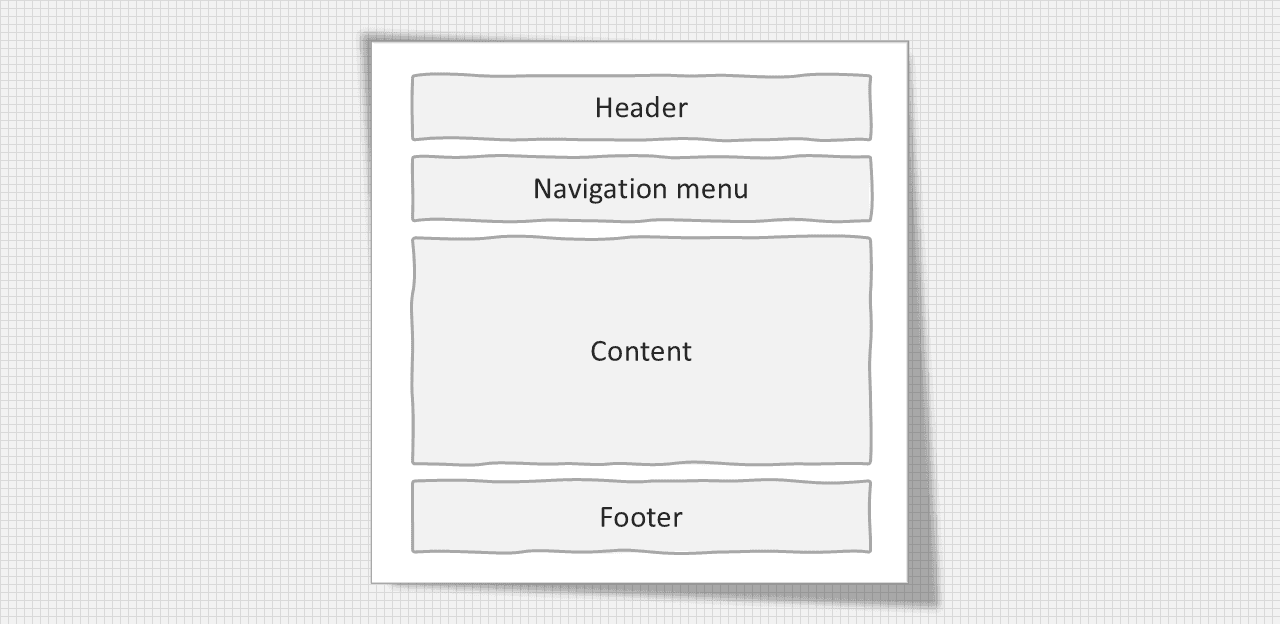
One column layout structure
Two column layout: This website layout is mostly used for tablet and laptops.
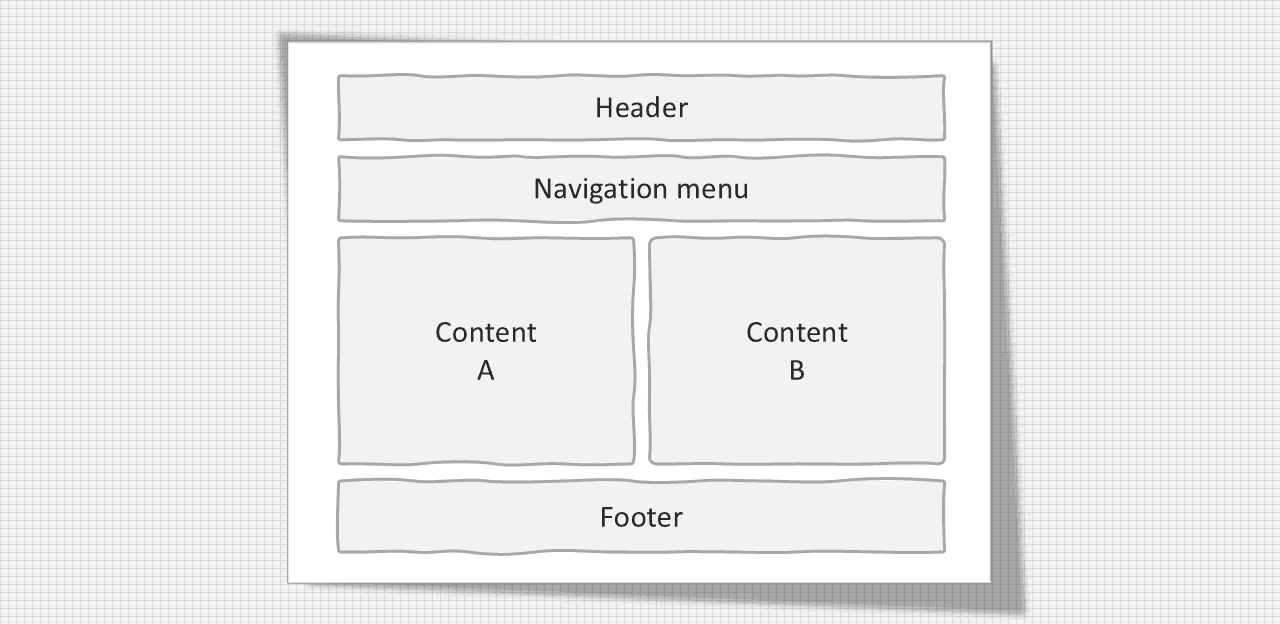
Two column layout structure
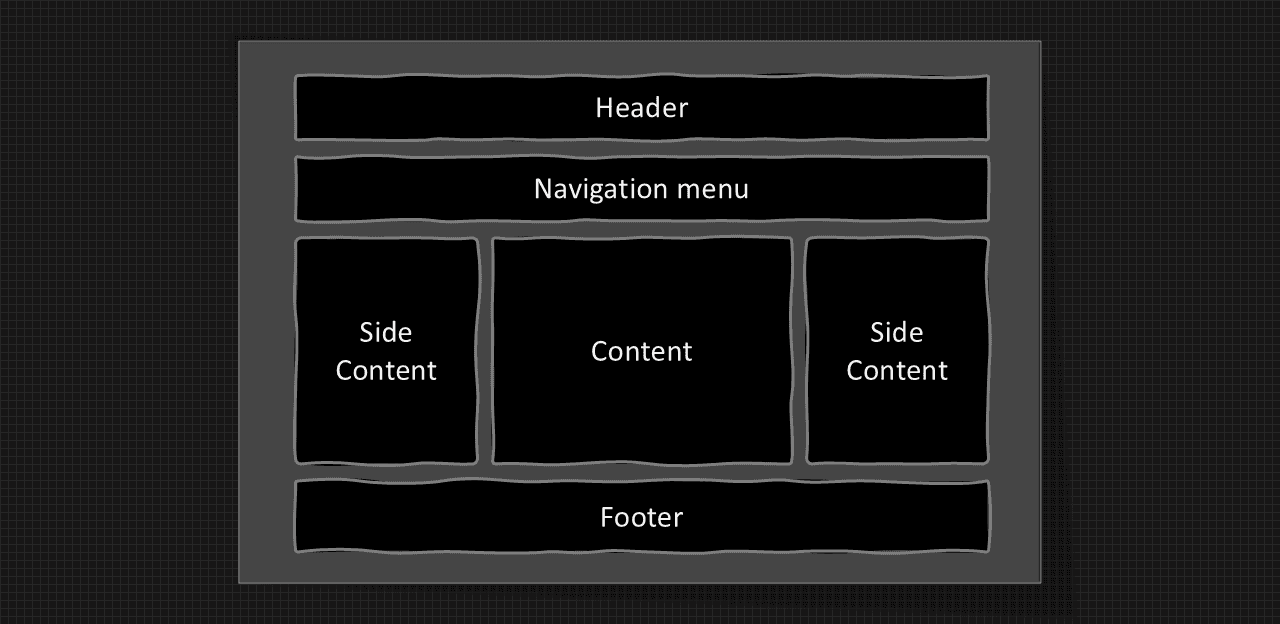
Three column layout: This website layout is mostly used for desktops.

Three column layout structure
Next Up
5: JavaScript
In the next chapter we will be Learn about the basic concept and uses of JavaScript programming language which are useful for the web development.
Start Chapter 5 ➔